Average Electricity Usage in a 3-Bedroom UK House
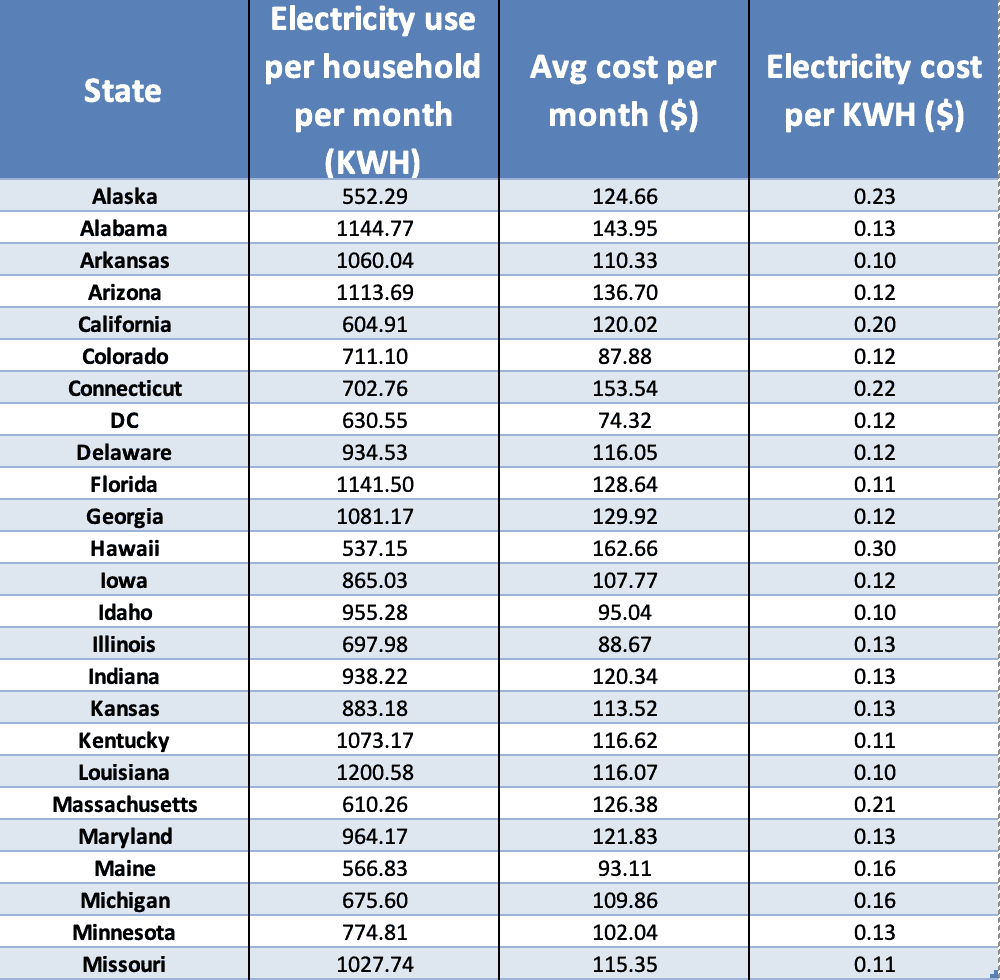
The average electricity usage in a 3-bedroom UK house is a complex issue, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and cost-saving measures.
Average Electricity Consumption by Appliance Type
A typical 3-bedroom UK house consumes electricity for various purposes, with the largest share going towards heating, followed by appliances and lighting.
- Heating: Central heating systems, including boilers and radiators, account for a significant portion of electricity usage, particularly during the colder months. The average household in the UK spends around £1,200 per year on heating, with gas being the primary fuel source. However, electric heating systems are becoming increasingly popular, especially in new builds and for individual rooms.
- Appliances: Domestic appliances like washing machines, dishwashers, ovens, and refrigerators consume a considerable amount of electricity. The energy efficiency of these appliances plays a significant role in determining their electricity consumption. Older appliances tend to consume more energy than newer, more efficient models.
- Lighting: While lighting accounts for a relatively small portion of overall electricity usage, it is still important to consider energy-efficient options. Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs can significantly reduce electricity consumption for lighting.
Factors Influencing Electricity Usage
Several factors influence electricity consumption in a 3-bedroom UK house, including household size, occupancy patterns, and energy efficiency measures.
- Household Size: A larger household will naturally consume more electricity due to increased appliance usage, lighting, and heating needs.
- Occupancy Patterns: The number of people living in the house and their daily routines significantly impact electricity consumption. For instance, a household with members who work from home or have children attending school remotely will likely consume more electricity than a household with members who work outside the home.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Implementing energy-efficient measures, such as installing double-glazed windows, insulating the loft, and using energy-efficient appliances, can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
Comparison of Electricity Usage, Average electricity usage 3 bedroom house uk
Comparing the average electricity usage of a 3-bedroom UK house to other dwelling types and international comparisons provides a broader perspective on energy consumption patterns.
- Comparison with Other Dwelling Types: A 3-bedroom house generally consumes more electricity than a 2-bedroom house due to its larger size and potentially greater occupancy. However, a 4-bedroom house might consume even more electricity, depending on the factors mentioned above.
- International Comparisons: The average electricity usage in the UK is relatively high compared to some other European countries, such as Germany and France. This difference can be attributed to various factors, including climate, housing stock, and energy policies.
Understanding Electricity Bills
Understanding the components of your electricity bill is crucial for making informed decisions about your energy consumption and finding ways to save money. A typical UK electricity bill consists of several key elements, each contributing to the overall cost.
Breakdown of Electricity Bill Components
The breakdown of a typical electricity bill in the UK includes the following components:
- Standing Charge: This fixed daily charge applies regardless of how much electricity you use. It covers the cost of maintaining the electricity network and supplying you with a connection. The standing charge is usually expressed in pence per day.
- Unit Cost: This is the price you pay for each unit of electricity you consume, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The unit cost is usually expressed in pence per kWh.
- VAT (Value Added Tax): At a rate of 5%, VAT is applied to the total cost of your electricity, including both the standing charge and the unit cost.
Electricity Bill Examples
Here are some examples of electricity bills for a 3-bedroom UK house with different energy tariffs and consumption levels:
- Example 1: A household with an average consumption of 3,000 kWh per year on a standard variable tariff with a standing charge of 25 pence per day and a unit cost of 18 pence per kWh would pay an annual bill of around £650. This includes £91.25 for the standing charge, £540 for the unit cost, and £28.75 for VAT.
- Example 2: A household with the same consumption on a fixed-rate tariff with a standing charge of 20 pence per day and a unit cost of 15 pence per kWh would pay an annual bill of around £530. This includes £73 for the standing charge, £450 for the unit cost, and £23.50 for VAT.
Interpreting Electricity Bills
To effectively interpret your electricity bill and identify potential savings opportunities, consider the following:
- Compare your bill to previous bills: Look for any significant changes in your consumption or cost. This can help you identify potential leaks or inefficient appliances.
- Analyze your usage patterns: Track your electricity consumption throughout the day and week to understand when you use the most energy. This can help you identify opportunities to reduce consumption during peak hours.
- Compare tariffs: Regularly compare different energy tariffs to ensure you are on the best deal for your needs. Consider factors such as standing charges, unit costs, and any special offers or discounts.
- Identify potential savings: Once you understand your electricity usage and tariff, you can implement strategies to reduce consumption and save money. This may include switching off lights when not in use, using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing your reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Reducing Electricity Consumption: Average Electricity Usage 3 Bedroom House Uk
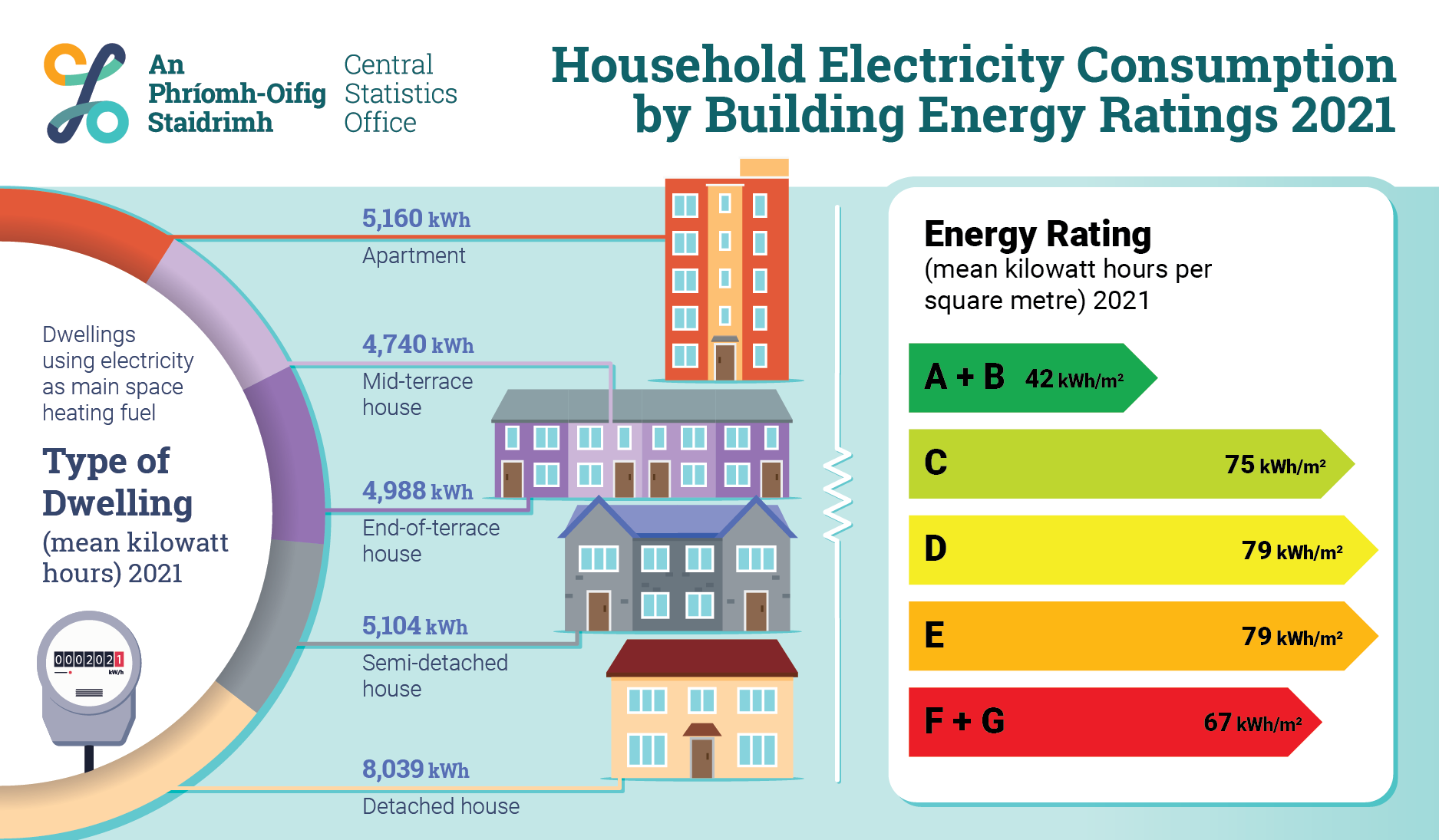
The average UK household can significantly reduce its electricity consumption through a combination of smart appliance choices, improved insulation, and conscious behavioral changes. By taking these steps, not only can you save money on your energy bills, but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Appliance Upgrades
Replacing older, inefficient appliances with modern, energy-efficient models can have a substantial impact on your electricity consumption. Modern appliances are often rated with an energy efficiency label, allowing you to compare the energy consumption of different models.
- Refrigerators and Freezers: Choose models with an A+++ rating, which are significantly more efficient than older models. Ensure your refrigerator is not positioned near a heat source, such as a radiator or oven, as this can increase energy consumption.
- Washing Machines and Dishwashers: Opt for models with an A+++ rating and use the eco-cycle settings to minimize water and electricity consumption. Consider using cold water washes whenever possible, as heating water consumes a significant amount of energy.
- Lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs. LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan, leading to long-term cost savings.
Insulation Improvements
A well-insulated home retains heat more effectively, reducing the need for heating and therefore lowering electricity consumption.
- Loft Insulation: Ensure your loft is adequately insulated to prevent heat loss through the roof. The recommended insulation thickness is at least 270mm. Consider upgrading to a higher level of insulation, such as 300mm or more, for even greater savings.
- Wall Insulation: Insulating your walls can significantly reduce heat loss and improve energy efficiency. There are various insulation options available, including cavity wall insulation, internal wall insulation, and external wall insulation. The best option for your home will depend on its construction and existing insulation.
- Draught-proofing: Seal any gaps or cracks around windows and doors to prevent cold air from entering your home. This can be achieved using draught excluders, weather stripping, or caulk.
Conducting an Energy Audit
An energy audit is a comprehensive assessment of your home’s energy usage, identifying areas where you can save energy and reduce your electricity consumption.
- Gather Data: Collect information on your energy bills for the past year, noting your average monthly consumption. Also, record the types and age of appliances in your home.
- Visual Inspection: Walk through your home and note any potential energy leaks, such as drafty windows or doors, gaps in insulation, or poorly sealed vents. Consider using a thermal imaging camera to identify areas of heat loss.
- Appliance Usage: Assess the frequency and duration of use for each appliance in your home. Consider if you can reduce the usage of any appliances, such as turning off lights when leaving a room or using energy-saving settings on your appliances.
- Behavioral Changes: Evaluate your daily routines and identify areas where you can reduce energy consumption. This could include turning off lights when leaving a room, using less hot water, or reducing the use of appliances like tumble dryers.
- Analyze and Implement: Based on the data gathered, identify areas for potential energy savings. Develop a plan to implement energy-saving measures, such as upgrading appliances, improving insulation, or making behavioral changes.
Cost-Effectiveness of Energy-Saving Measures
| Measure | Upfront Investment | Long-Term Savings (per year) | Payback Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED Lighting Upgrade | £50-£100 | £50-£100 | 1 year |
| Loft Insulation | £500-£1000 | £100-£200 | 2-5 years |
| Cavity Wall Insulation | £1000-£2000 | £200-£400 | 2-5 years |
| A+++ Rated Refrigerator | £500-£1000 | £50-£100 | 5-10 years |
| A+++ Rated Washing Machine | £400-£800 | £50-£100 | 4-8 years |
Note: The payback period is the time it takes for the cost savings from an energy-saving measure to equal the initial investment. These are approximate figures and actual savings may vary depending on factors such as energy tariffs, usage patterns, and the specific model of appliance.
Average electricity usage 3 bedroom house uk – While an average 3-bedroom house in the UK consumes a significant amount of electricity, there are simple ways to reduce your energy footprint. Consider the details, like choosing timeless fixtures for your bathroom. The warmth and character of bright brass bathroom fixtures can create a welcoming space while still being eco-conscious.
These small changes can add up to a significant impact on your energy consumption, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
While the average electricity usage for a 3-bedroom house in the UK can vary depending on factors like insulation and appliance usage, consider exploring the potential of a bungalow design for energy efficiency. If you’re looking for a more compact and potentially lower-energy footprint, bungalow plans for 3 bedrooms offer a unique approach to home design.
With careful planning and smart choices, you can build a home that not only meets your needs but also minimizes your environmental impact, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.